What is a Pacemaker?
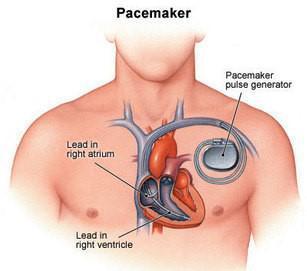
A pacemaker is a small device that helps to control abnormal heart rhythms. It is placed in the chest or abdomen area. It is used to treat arrhythmias (a problem with rhythm or rate of the heartbeat). A heartbeat of a person can be too fast or too slow during arrhythmia. So, the pacemaker is used to relieve some arrhythmia symptoms such as fainting, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Pacemakers use low-energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate. It can also monitor your breathing, blood temperature & other factors and then adjust your heart rate accordingly.
To whom pacemaker is offered
The pacemaker is offered to the person who is suffering from arrhythmia. Arrhythmia is a disease in which the person’s heart beats too slow or too fast. During this heart is unable to pump enough blood to the body. When the person’s heart beats fast, it is said as tachycardia & when the heart beats too fast, it is noted as bradycardia.
When the arrhythmia is not treated by medication, the cardiologist will suggest you go for pacemaker surgery as it can control your irregular rhythms of the heart.
What are the different types of pacemakers?
Your cardiologist will prescribe you the pacemaker according to your heart condition. There are three basic types of pacemakers, and they are as follows.
1. Single chamber pacemaker
In a single-chamber pacemaker, only one lead is attached to both the lower (right ventricle) & upper chamber (right atrium) of the heart.
2. Dual-chamber pacemaker
In a dual-chamber pacemaker, two leads are separately attached to the lower (right ventricle) & upper chamber (right atrium) of the heart.
3. Biventricular pacemakers
Two or three leads are separately attached to both the lower (right ventricle), upper chamber (right atrium), and the heart’s left ventricle in a biventricular pacemaker.
Advantages of pacemaker surgery
The following are the advantages of pacemaker surgery
- ● It is less invasive
- ● It provides AV synchrony
- ● It increases the survival rates
- ● Facilitate regular heartbeat
- ● It lowers the risk of systemic embolism and stroke
- ● It reduces the chances of congestive heart failure
Complication or risk associated with pacemaker surgery
The following are the complication or risk that one can suffer after the pacemaker surgery
- ● Infection where the pacemaker is implanted
- ● Swelling at the area where the generator is placed
- ● Damage to your nerve or blood vessel
- ● Collapsed lungs
- ● Allergic reaction from the anaesthesia
- ● Excess bleeding
Indication for pacemaker placement
The common indication for pacemaker placement includes the following
- ● Sinus node dysfunction
- ● Acquired AV block
- ● Post myocardial infarction
- ● Congenital complete heart block
- ● Long QT syndrome
- ● Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- ● Heart failure
How does a pacemaker work?
A pacemaker consists of a computerised generator, battery, and electrodes. Electrodes are the wire with the sensor at the end of the pacemaker. The electrodes detect your heart’s electrical activity and send data through the wires to the computer in the generator.
If your heart rates are found abnormal, the computer will direct the generator to send electric pulses to your heart. The wire transfers the electric pulses to your heart.
DO’s and don’ts before the pacemaker surgery procedure
- ● Do not eat or drink anything for several hours before the surgery
- ● Blood thinner drugs can increase the risk of bleeding during the procedure; consult with your physician when you should stop taking the blood thinner and resume taking it after the process.
- ● Tell everything to your cardiologist about every medicine you are taking.
The procedure of pacemaker surgery
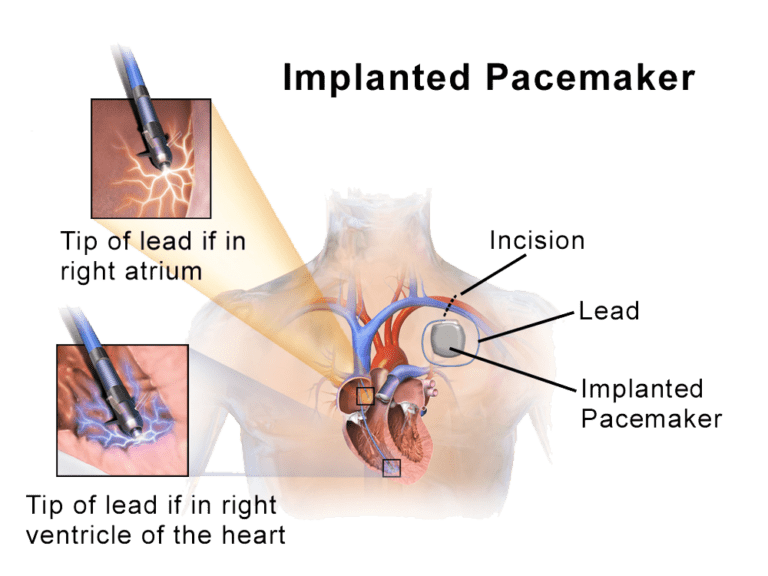
The whole procedure of placing a pacemaker might take 1 to 2 hours. Your anesthesiologist will examine your health and then give you the anaesthesia before the pacemaker surgery. Only the area of the incision is numbed. Your cardiologist will provide you with medicine to keep you relaxed.
After that, your cardiologist makes a small incision in the upper chest, under the collarbone. The incision can be 2-3 inches long. With the help of fluoroscopy, your doctor places the leads (wire) of the pacemaker to your heart chambers.
After this, the cardiologist rechecks the leads placed in the right place or not. The next step is to create a small space under the skin to fit a pulse generator. The generator is fixed under the skin of the chest. The leads of the pacemaker are then connected to the generator. At last, the doctor closes the incision and covers it with gauze to keep it clean. After the surgery, the nurse will check your pulse, blood pressure, and heart rhythm…
Do’s and don’ts after the pacemaker surgery.
After the surgery, it is the recovery stage and you should be more careful. Here are the do’s and don’ts that will help you to recover fast
- ● You should not lift heavy objects…
- ● Walk, exercise or bath according to the instruction of your doctor
- ● Do wear clothes that are comfortable to you (avoid tight clothing)
- ● Take all your medicine as prescribed by your doctor
- ● Eat healthy diet
- ● Immediately consult your doctor is facing with pacemaker problem
- ● Don’t allow magnetic things near your pacemaker, as that can disrupt the function of your pacemaker
Recent Posts
- All Posts
- Blog
Read More
Our Speciality
- Cardiology & Cardiac Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Orthopedics & Joint Replacement
- Urology
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology & Dialysis
- Bariatric & Metabolic Surgery
- ENT & Head Face Neck Surgery
- Internal Medicine & Critical Care
Explore More
Our Doctors

Dr Prakash Chandwani
(Chief Managing Director) Director & Head Dept of Cardiology

Dr Mahesh Goyal
Director & Head Dept of Allergy Specialist, Asthma & Sleep

Dr Mohammed Sharif
CEO & Global Operations

Dr Ghanshyam Agrawal
Consultant Dept of Neuro Surgeon

Dr Sumit Kamble
Consultant Dept of Neurology
See All Doctors


